Banking systems have become the backbone of the modern economy all around the world. The extent of their influence in any given economy in any country cannot be overstated.
Though in terms of sheer numbers, this large network of banks mostly includes commercial banks. Thousands and thousands of them – in some cases only in one country.
But in terms of power and influence, the pinnacle of this system is of course occupied by central banks.
Central banks have perhaps the most important monetary and fiscal responsibilities and influence. In this article we want to bring central banks under our magnifying glass for a closer look at what they are and what they do.
What Is a Central Bank? Do All Countries Have One?
As it is often said, the devil is in the details. This is also true for our case. Because a central bank, as the name suggests, can be defined as the center of a centralized system of banking and finances in any given fiscal territory.
As the main and ranking authority, a central bank is tasked with various major responsibilities and duties, the likes of which cannot be seen with commercial banks.
Also Reading: How Do Central Banks Affect the Forex Market?
Given the current economic structure of the world, it can be said that all countries in fact have a central bank. In most countries, it is directly known as the central bank of that country, followed or preceded by the name of that country. And in other countries it might have a different name. For instance, the central banking authority in the US is known as the Federal Reserve; and in the UK the central bank is referred to as the Bank of England.
Whatever name or title they may assume, central banks have by and large the same duties, which we will discuss in the following parts.
Duties and Responsibilities of Central Banks
So what are the actual responsibilities of central banks?
If you ask the average joe, their understanding of what banks do in general, would fall mostly within the domain of a commercial bank – i.e. a place where you can deposit and withdraw money, get loans and mortgages, and basically manage finances.
But central banks have far more important duties. They are in charge of defining the country’s monetary policies, affecting commercial banks and their customers alike.
Furthermore, central banks are in charge of the regulation of physical money circulation. They can inject liquidity in the form of coins or banknotes and bills into the economy, thus adjusting the amount of liquidity and money in circulation. This can also indirectly impact many other economic factors, including inflation.
Central banks may also be tasked with observing and regulating the operations of commercial banks and also issue high volume loans to them, which then commercial banks can provide to their customers at different interest rates.
But in this article we want to mainly focus on the policies that are set by central banks and their impact on economies.
What Policies Are Set by Central Banks?
As was briefly discussed in the last section, any central bank assumes many important financial responsibilities, all of which are absolutely essential for the economic health of that country. But among the most important policies set by central banks, we can refer to monetary policies.
What Are Monetary Policies and What Is Their Purpose?
So far, it can be summarized that the main role of a central bank is to ensure the overall health of the economy. This process is in fact carried out with the help of these monetary policies.
As such, monetary policies can be defined as a number of tools and strategies that are implemented by central banks to ensure the economy is working properly and also to maximize growth and other important economic indicators such as the GDP.
Of course, as it can be guessed, the central banks also need to be able to manipulate other major economic indicators such as inflation and even employment rates.
Inflation and deflation are controlled via monetary policies in the form of providing or not providing the economy with liquidity, thus increasing or decreasing the amount of actual money in circulation, which is directly linked with inflation and deflation.
Employment and unemployment rates are also at the mercy of central banks, since certain monetary policies can favor the market and business, thus creating a boom in their operations. This will, in turn, lead to higher employment rates. The opposite is just as true. However, that would be more of a byproduct and less of a direct aim, naturally.
Now that we know what monetary policies can do, let’s see how many different types of such policies there are.
What Are the Different Types of Monetary Policies?
types monetary policy
Central banks have a de facto authority to issue monetary policies whenever they see fit, or rather, whenever most required by the status quo of the economy.
Now, based on the status quo, there are two opposing monetary policies that can be issued by the economies, in order to either push forward or pull backwards in a way.
These two types are mainly known as contractionary policies and expansionary policies.
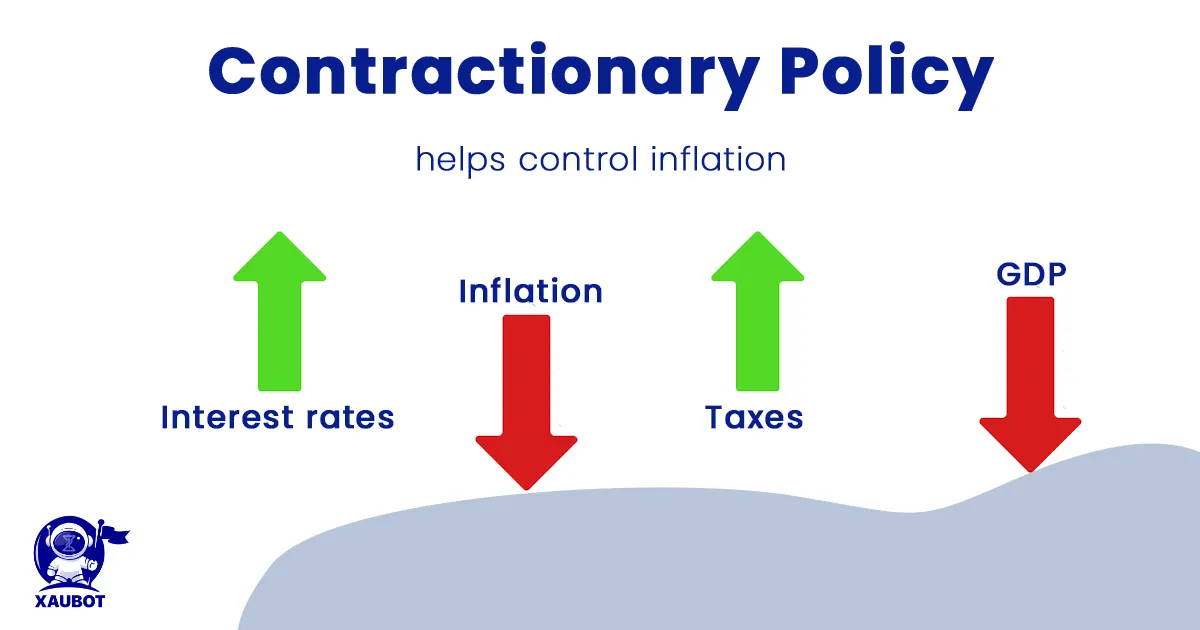
Contractionary Policies
Contractionary Monetary Policy
Such policies will contract or decrease the momentum of the economy, because it is deemed to be headed toward an undesirable direction. Such direction can be defined in terms of mostly inflation, above all. So with the help of contractionary policies, central banks can slow down the economy and limit the supply of liquidity. Most importantly, increasing interest rates fall within this category, which might have the most important impact on financial markets, including the foreign exchange or the forex market.
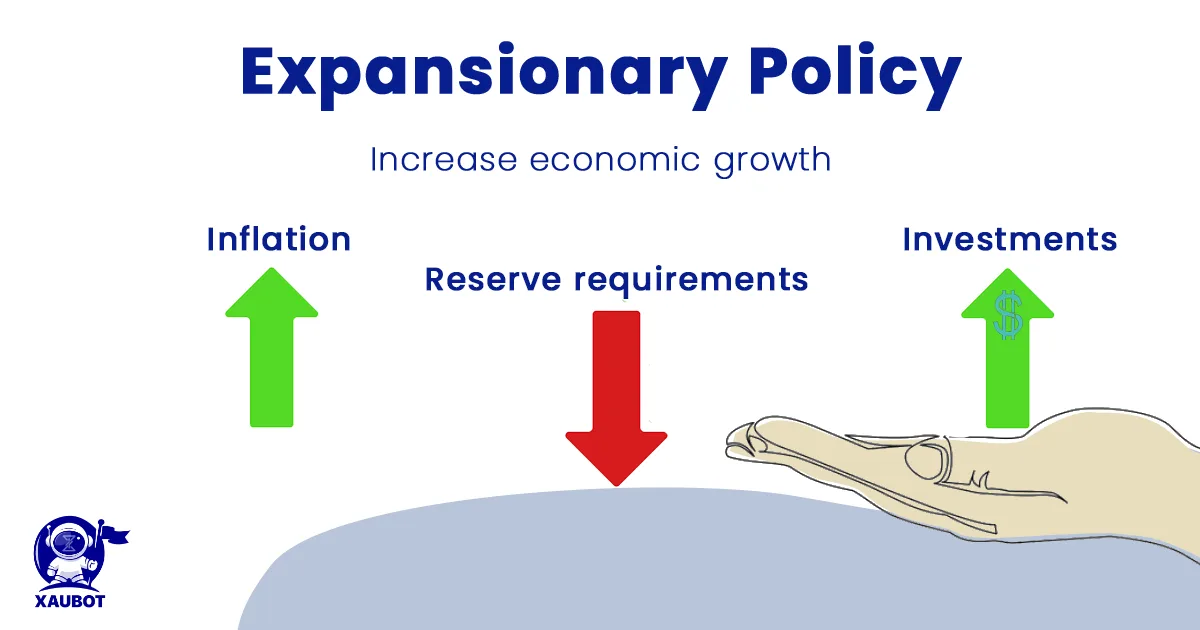
Expansionary Policies
what is expansionary policy
Standing opposite contractionary policies are expansionary monetary policies. Their aim is to expand or increase the momentum of the economy at times when it is slowing down or headed toward the wrong direction. In this case the wrong direction or condition can be defined in terms of economic recession. So in order to boost the economy, central banks can opt for expansionary policies which include decreasing interest rates so that consumers would have more access to bank loans which then can be used either to increase their spending power or be used in the financial markets of the economy.
How Are Monetary Policies Enforced?
So what are the means by which central banks can enact and enforce their monetary policies?
In essence, there are two main ways or tools that central banks use to realize their monetary policies:
Interest Rates
This is one of the most important figures set by the central bank in any country. It heavily and directly impacts the customers of commercial banks. Interest rates define the rate of interest for the loans given to commercial banks by the central bank and also the loans given to customers by commercial banks.
Commercial Bank Reserves
Central banks may also adjust the amount of reserves that commercial banks ought to hold. This so-called reserve is the percentage of the customers’ deposits that is kept and not allocated by the commercial bank. Decreasing the level of this reserve will give more resources to commercial banks to allocate to their investments and operations.
Conclusion
A central bank is the main authority in setting the monetary policies of any economy. Such policies can immensely and directly impact that direction of the economy and all that it encompasses, including of course the consumers, spending power, inflation, recession, financial markets, exchange rates, etc.
The decisions that are made by central banks are extremely wide-encompassing in their circle of influence. Together with the fiscal policies that are set by the government, such monetary policies define the future of any economy.
FAQ:
Q: What is a Central Bank?
A: A Central Bank is a financial institution that is responsible for implementing monetary policy, regulating banks and financial institutions, and issuing currency in a country.
Q: What is monetary policy?
A: Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by a Central Bank to manage the supply and demand of money in the economy. It includes setting interest rates, controlling the money supply, and regulating the financial system to achieve specific economic goals, such as price stability and low unemployment.
