Going long, shorting, fractional pip range, lot size, margin, scalping, trading leverage, and the whole arsenal of forex terminology that you must know in order to be able to learn more and become a more experienced forex trader.
Let’s face it, if you don’t speak the language, how do you expect to learn anything from any given environment? In order to understand other, more seasoned traders who would be willing to impart their knowledge and wisdom to the next generation of forex traders, you need to familiarize yourself with the basic forex terms and jargon.
That is why in this article, we want to take you through 20 of the most important forex terms.
List terms of Forex Trading Terminology:
| Forex Trading Terminology Terms |
|---|
| Trading Pair |
| Ask Price |
| Base/Quote |
| Bid Price |
| Ask Bid Spread |
| Pip Range |
| Fractional Pip Range |
| Lot Size |
| Equity |
| Margin |
| Stop Loss |
Trading Pair
In the forex market, we trade foreign currencies, or more precisely we make speculations on their spot prices. As such a trading pair or a currency pair is made up of two currencies. In any given pair, the first pair is called the base currency and the second is called the counter or quote currency. So, for instance, in the pair GBP/USD, we speculate the price of the British pound against the price of the US dollar. Together they form a currency pair. Forex markets offer numerous currency pairs.
Base/Quote
In any currency pair, we have two foreign currencies. For example, in the case of GBP/USD, we have the US dollar and the British pound. The first currency in any pair is called the base. On the other hand, the second currency in any pair is called the quote currency (also called the denominator).
Ask Price
The ask price, which is also called the offer price, indicates the price at which traders can purchase the base currency in a trading pair in exchange for the quote currency. For example, in the pair EUR/USD the ask price would indicate how much Euro you can buy in exchange for the US dollar, or denominated by the US dollar. As of the time of writing this article, the ask price for EUR/USD pair is 1.07 – this means for each Euro you need to pay 1.07 US dollars.
Also read: Forex Indicator Type
Bid Price
In contrast to ask price, bid price is the price at which you can sell a currency pair. Of course, the base and quote currencies are also taken into consideration here. For example, in the pair EUR/USD the bid price would refer to the price at which you can sell the base currency in this pair, which is Euro, and receive the quote or counter currency, which is the US dollar. As a general rule, bid price is always lower than the ask price, which is the same for all foreign exchange pairs and markets.
Ask Bid Spread
The difference in the ask price and the bid price is known as the spread. The spread is where brokers actually make their money. Because they do not receive money directly from traders, the difference between the price of buying and selling is where they make their profits.
Pip Range
The term pip indicates the amount of change in the price of a given currency pair. In fact, 1 pip is the smallest amount of change that a currency pair can have. The price (or quote) of each currency pair has four decimal points. Therefore, for example, if the quote for a pair is 2.3456 and the price goes to 2.3458 then it can be seen that the price movement is equal to 4 pips.
Fractional Pip Range
In certain cases, currency pairs can have one extra decimal point. This means that instead of the usual four decimal points, they would have five decimal points – i.e. instead of 2.3456 it would be 2.34567. When the price has five decimal points, the changes are counted in fractional pips. So, for example, if the price goes from 2.34567 to 2.34568, then we say the price movement is equal to one tenth pip (as opposed to one pip).
Lot Size
In forex markets, trades have standard sizes. The standard unit or lot size for trades in forex is 100,000 units. However, there are other smaller lot sizes that are called mini, micro, and nano – respectively equal to 10,000, 1,000, and 100 units.
Pip Value

Pip value in Forex Trading Terminology
Since pip shows the amount of change in any given currency pair, the pip value shows the worth and value of 1 pip. How much is that pip range worth for your trade? In order to find the answer to this question, you need to multiply the pip value by your lot size.
For example, if the currency pair’s quote for EUR/USD goes from 1.2345 to 1.2346 this 1 unit of pip is equal to 0.0001 dollar. So for the standard lot size of 100,000 units, i.e. if you are trading with 100,000 dollars, this 1 unit of change would have a value of 100,000 x 0.0001 which is equal to a pip value of 10 US dollar in this trade for you.
It is very important to note how much the pip value is for you in your chosen lot size.
Equity
Equity refers to the entire amount of money you have in your trading account – this would include both your profits and also your losses.
Margin
Margin trading in Forex Trading Terminology
In order to open a position, you will need a minimum amount of funds. That minimum amount of funds in order to open a certain position is referred to as margin.
Margin is shown in percentages. So, for example if you trade on a margin of 1% this means you always need to deposit 1% of your chosen lot size. How can you trade the whole standard lot size with only a margin of it? In the case of margin trading, you are trading based on a loan from the broker and the only so-called down payment is the margin that you deposit.
Free and Used Margin
Free margin refers to the available amount in your trading account that you can put up as the margin percentage. On the other hand, used margin is the portion of your deposit that you have used as the margin and it is being held by the broker.
Margin Call
If you have an open position based on a margin that you have deposited earlier, and the position drops to or further than your margin, the broker will notify you to increase your margin and deposit more. This process is known as the margin call.
Trading Leverage
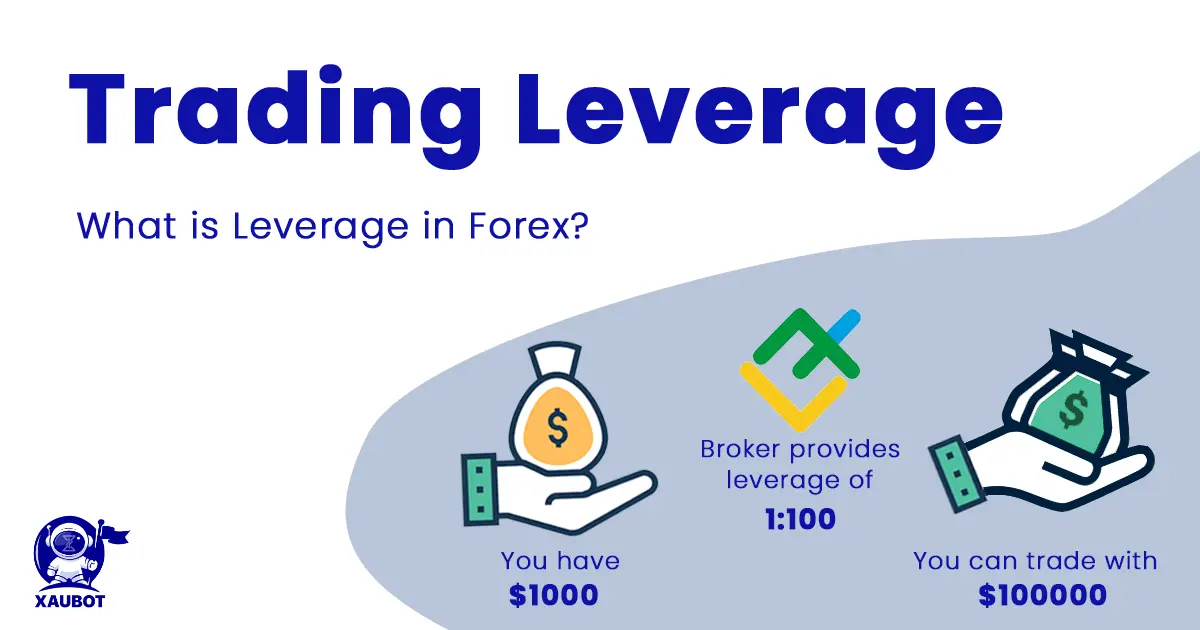
Leverage in Forex Trading Terminology
Leverage is in essence the money that the broker will loan to you in order to trade with. Depending on the broker, this proportion can defer. You will deposit a certain percentage of the leverage, which is called the margin, and the broker will give you a leverage to trade with. For instance, with a deposit of $1,000 you might be able to trade with $20,000 of funds.
Also Reading: How Leverage Works in Forex?
Trading Position
When you open a trade, it is called a position. So as long as you keep a trade open, that is the position.
Long Position
A long position refers to when a trader will purchase the base currency. So, basically buying is called taking a long position. In our currency pair example of EUR/USD the long position would be when you purchase Euro in exchange for the US dollar.
Short Position
A short position is referred to selling the base currency. So for instance, if you are shorting EUR/USD it means you are selling Euro in return for the US dollar.
Closing
When the trader is in a long position, and the price of the base currency goes up, in order to yield the benefits, the trader would then attempt to close.
Opening
When you take a position whether long or short, you are opening a position. The action of assuming that position for a trade is called opening a position.
Stop Loss
stop loss in Forex Trading Terminology
In order to avoid too much loss, you can set a certain amount for your trade and your position to close when the price falls down too much. So when the price decreases and hits a certain threshold set by the trader, the trade would automatically close in order to avoid further loss.
Q: What is a currency pair?
A: A currency pair is the quotation of two different currencies, with the value of one currency being quoted against the other. For example, EUR/USD is a currency pair that represents the value of the euro against the U.S. dollar.
Q: What is a pip?
A: A pip (short for “percentage in point”) is the smallest unit of measurement for a currency pair’s price movement. It is usually the fourth decimal place in a currency pair’s price quote, except for currency pairs involving the Japanese yen, where it is the second decimal place.
