In this article we want to go through the structure of the forex market. As with other features that are particular to the foreign exchange market, the structure of the forex market is also unique in its own sense.
First we will start with a conventional financial market structure and then move on to the details of forex.
Conventional Financial Market Structure
As an example of a conventional financial market we can refer to the stock market. In fact, stock markets are what the general public would think of first when discussing financial markets.
The typical structure of a stock market would have three pillars:
- Centralizes entities overseeing the trades (i.e. stock exchanges)
- Buyers
- Sellers
This is how most financial markets are structured. There is a centralized entity and place where buyers and sellers can convene, either physically or virtually, and engage in the process of purchase and sale of specific assets and commodities.
So, what’s so special about the structure of forex?
What Makes the Structure of Forex Unique?
The main aspect of the forex market that sets it aside from most other financial markets is its decentralized nature. The forex market is comprised of decentralized or over the counter (OTC) markets around the world where foreign exchange trades take place.
With this decentralized nature comes the next step in the forex peculiarity. Because of the OTC markets that operate to form the whole body of forex, a large number of various participants have been attracted and are operating in the forex market.
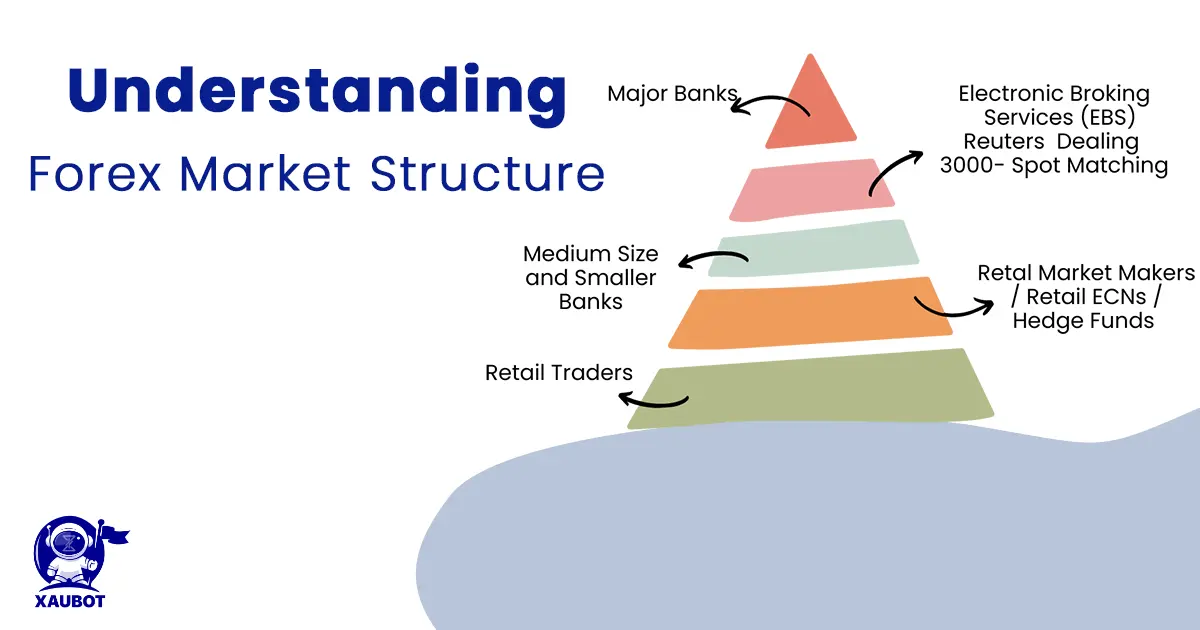
These participants include giant banking systems and even governments all the way down to individual traders. Let’s take a look at their relation with regard to one another.
The Structure of Forex Participants and Their Relations
As was mentioned above, there are many peculiarities to the forex market structure and the decentralized structure of the market has attracted various players.
Similar to most other financial markets, individual traders make up the majority of the participants of forex markets with regard to numbers.
Another group of participants in the forex market are banks, both central banks from all countries and also commercial banks from around the world.
In fact, banks are responsible for most of the money that is traded in FX markets.
Apart from individuals, central banks, and commercial banks, there are many other big participants including governments, hedge funds, VCs, brokers, and various businesses and international corporations.
Now that we are done with participants, we get to the next portion of the forex market structure – the assets that are actually traded.
Peculiarities of Traded Assets: Foreign Currency Pairs
In any financial market, the number of assets or commodities that can be traded is of course limited and as the participant in the market you might have a general understanding of what you are dealing with.
In the case of forex, however, there is an astoundingly great number of currency pairs available for trading. For instance, if you are using the most popular forex trading platform which is MetaTrader, you might get lost in the currency pairs in your trading terminal.
Let’s discuss how you can navigate your way among these currency pairs to choose the best one for trading.
Picking the Right Currency Pairs to Trade
In this portion of our discussion, the decentralization of forex also comes to play. Depending on which trading terminal you use, or which market around the world you are trading in, then the currency pairs would vary.
However, the most important factor when it comes to picking the best currency pair to trade is your own trading strategy. Though there are other considerations to keep in mind. But first, more on the pairs themselves.
What Are Bid and Ask?
In any given currency pair, one currency is thought of as the bid which is technically bought and the other currency as the ask which is sold.
So for example, in a currency pair such as USD/GBP, US dollar is the bid and the British pound is the ask currency.
There is another notion with similar sounding terminology known as the bid ask spread.
So what is the bid ask spread? In essence, the bid ask spread is the difference between the price of the bid and the price of the ask.
Let’s consider the currency pair USD/GBP. If you take a look at this pair in your trading terminal and notice the bid ask spread, you will see that the bid price is the price at which your broker is willing to pay to purchase the base currency (USD in this case) in exchange for the counter currency (which is GBP in this example).
On the other hand, the ask price is conversely the price at which the broker is willing to sell the base currency in exchange for receiving the counter currency.
So far in our discussion of the forex market structure, we have cleared many terminologies, including currency pair, base and counter currency, bid and ask price, and bid ask spread. Now, let’s see which currencies are the most popular ones.
Most Traded Currency Pairs
As was mentioned above, there are countless currency pairs in the forex market and it might be a bit difficult to navigate through them when attempting to begin forex trading.
Among all the considerations, trading volume might just be the most important one. So which pairs have the highest volume? And why is this important?
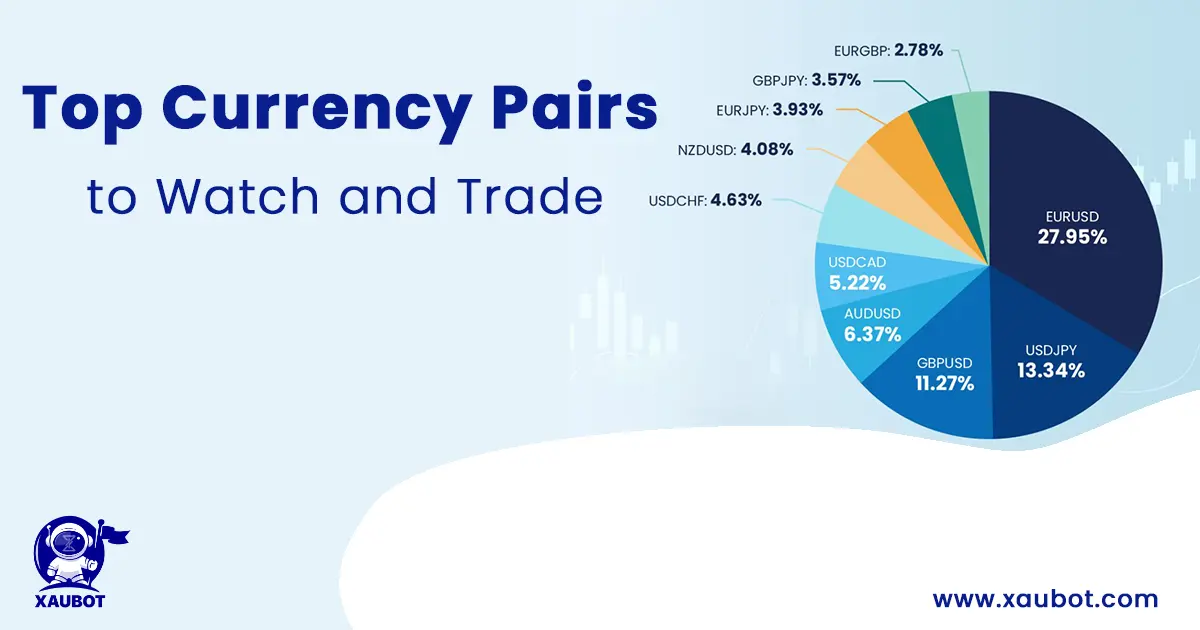
Although there are so many pairs, a certain and limited number of them are responsible for the majority of the trading volume.
In a nutshell, the currency pairs with the highest trading volume are as follows: USD/GBP, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, AUD/USD, and USD/CAD.
Put together, these currency pairs make up for more than 60% of all the trading volume of forex. Let that sink in for a second – 60% of forex trading volume would be equal to approximately $5 billion a day.
So why is popularity, i.e. trading volume, important in a trading pair?
Basically, the higher the trading volume for a trade, the higher the liquidity of that pair. Now we need to pose another question. Why is higher liquidity important?
When the liquidity of a trading pair is high it means that certain pair can be bought and sold much more quickly. This allows for much faster execution of trades, whether it is a purchase order or going short (selling). So keep an eye out for currency pairs with high liquidity when deciding which pair to trade.
More on Forex Structure: Lot Size, Going Long & Going Short
Another term that you might hear a lot with forex trading is lot size.
A lot size refers simply enough to the size of the trade, or rather the amount or unit of assets that you take to the trade.
There are standard lot sizes in forex – in fact that standard forex lot size is 100,000 and it means you need 100,000 units of a currency to enter into a trade.
It may sound a lot, especially if we are talking about currencies such as the US dollar, Euro, or the British pound.
This is why there are also other lot sizes in forex available for trading, which are known as mini, micro, and nano – respectively equal to 10,000, 1,000, and 100 units.
So for instance a micro lot size will allow you to trade with smaller amounts rather than other lot sizes.
In terms of actually taking a certain position, you can go long or short.
Basically, going long means purchasing the base currency in a currency pair, mainly because you are feeling bullish on it, predicting that its price will appreciate in time.
By contract, going short means you are selling the main or base currency in a pair in exchange for the counter currency, because you are feeling bearish about the base currency, predicting that it will depreciate in value in time so it would be opportune to sell it off.
Conclusion
When it comes to the structure of the forex market, there are certain similarities between the foreign exchange market and many other financial markets.
However, there are many unique features in the structure of the forex. These features include the most fundamental structure of the forex, which is a network of decentralized or over the counter markets around the world. In addition to that, we have various participants in the forex market and also the countless currency pairs available for trading.
And of course in the matter of actually trading in forex, there are other features to take into account with regard to the specific structure of the market.
FAQ:
Q: What is the Forex market structure?
A: The Forex market structure refers to the way the Forex market is organized and operates. It includes the various market participants, trading instruments, and trading platforms.
Q: Who are the participants in the Forex market?
A: The Forex market has several types of participants, including banks, corporations, governments, central banks, retail traders, and institutional investors.
Q: What are the trading instruments in the Forex market?
A: The primary trading instruments in the Forex market are currency pairs. Traders buy and sell one currency against another currency with the aim of making a profit from the exchange rate fluctuations.
Q: What are the major currency pairs?
A: The major currency pairs are the most traded pairs in the Forex market. They include EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, and USD/CHF.